Abstract: India officially joined the G20 on September 26,1999. Since than India has been an active participant in G20’s discussions on global economic and financial issues. Last 25 years (1999-2024) highlight its role on inclusive and sustainable global future. A remarkable turning point has come when India holds the presidency of the G20 from 1 December 2022 to November 2023. India’s G20 presidency in 2023 came at a significant moment, as the country’s leadership was aligned with the vision of Amritkaal (The Era of Elixir) and the mandate of G20 presidency focus on development and growth. India’s External Minister S.J. Shankar well expound that the motto of us hosting the G20 is about getting the world ready for India, that means India’s evolving role in global affairs, it strengthens the need for the global community to recognize and accommodate to India’s growing influence, contribution and aspiration. Other important aspect is that the world has to be prepare for this new thinking that India has the potential to find real solutions to problems such as these geopolitical rivalries, climate change and environmental crises, rising inequality and human rights, global security and terrorism, global economic instability. And India ready for the world, it underscored the massage that the nation’s preparedness to global opportunities and challenges.It reflects India’s transformation into a dynamic, forward-thinking and global competitive player. This article’s purpose is to discuss how India, during its G-20 presidency very effectively presented solutions to the current global complexities, and through the theme of India’s G20 presidency Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam India left the massage on how the world and India complement each other ?
Keywords: G20, Global North, India, Development, World
Introduction
After the Asian financial crisis of 1997-98, the G20 was constructed in 1999 to promote global economic cooperation. The world’s leading industrialized and developing nations, along with their finance ministers and central bank governors, came together to begin the G20 as an informal forum.Its primary goal was to foster conversation and mutual assistance on issues related to multinational economic affairs stability. Over the years,the G20 has emerged into a significant platform for global economic governance. As of 2023, the group includes 21 members – 19 individual countries and 2 regional organizations, with the African Union being the most recent addition.Collectively ,G20 members account for approximately 85% of global GDP, over 75% of international trade, and around two-thirds of the world’s population, highlighting the group’s central role in framing international economic policies.
India assumed the presidency of the G20 from Indonesia on December 1, 2022, marking a pivotal moment in the nation’s international leadership. For the following year, India led the discussions and initiatives of the G20 under the overarching theme: “Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam”, a Sanskrit phrase meaning “One Earth, One Family, One Future.”(Our priorities will focus on healing our earth, creating harmony within our one family, and giving hope for our one future. It is also emphasis the importance of global solidarity, environmental responsibility and inclusive growth). As global challenges become increasingly complex, the role of the G20 remains crucial. India’s presidency reaffirmed the importance of multilateral cooperation and offered a model of leadership rooted in the ancient wisdom of unity and shared destiny.
India’s G20 Priorities
- 1.Green Development, climate Finance & Lifestyle For Environment (LiFE)
- 2.Accelerated, Inclusive & Resilient Growth
- 3.Accelerating progress on Sustainable Development Goals(SDGs)
- 4.Technological Transformation & Digital Public Infrastructure
- 5.Multilateral Institutions for the 21st Century
- 6.Women-led Development
During India’s G20 presidency, Prime Minister Narendra Modi emphasized a pragmatic approach to address in global challenges. India’s G20 Presidency in 2023 marked a defining moment in its journey toward global leadership. By focusing on inclusive development and championing the concerns of developing nations, India positioned itself as a bridge between the Global South and developed economies. India’s experience perspectives offer a rich source of insights for global challenges. As a key player in the G20, India not only stands to benefit from international cooperation but also has much to offer in shaping a more equitable and sustainable world order. The interconnected challenges facing the world today economic inequality to climate change leading such an influential group of countries has offered India a platform to drive meaningful change. India has vast experience in addressing challenges of poverty, innovation, and sustainability, and as G20 member states position themselves to tackle these urgent issues at the G20 summit in New Delhi in September 2023, India can leverage its own experience to promote inclusive development in various ways.
India’s Focus on Multilateralism
India’s G20 presidency highlighted the involving dynamics of multilateralism, where global problems require collective solutions. During the launch of India’s G20 Presidency theme 2023, Prime Minister Narendra Modi said “India’s G20 Presidency will work to promote a Universal sense of Oneness. Hence, Our theme – One Earth, One Family,Our Future- is a call For multilateral solutions to shared challenges.” India is a member of several multilateral institutions (UN, IMF, ADB, IAEA, OPCW, BRICS, SCO, BIMSTE, APEC, NAM etc) across various domains reflecting its active participation in global governance.The G20 Lifestyle Principles for Sustainable Development were endorsed by India in the Declaration and Think 20 and The G20 Idea Bank has multilateral reforms as one of his priorities. India’s campaign for reformed multilateralism gets attraction when the African Union is included into the G20.The G20 Declaration highlight the value of security and peace, with a particular emphasis on reforming the UN security council.The core mandate of G20 remains to promote economic growth and development. Prime Minister Narendra Modi has made it clear that these goals can not be achieved with out addressing the concerns and achieving a consensus in the Global South.
African Union as a new member in India’s G20 Presidency
The incorporation of the African Union (AU) as a permanent member of the G20 stands as one of the most noteworthy accomplishments of India’s G20 Presidency. During the inaugural session of the G20 Summit on September 9, 2023, Prime Minister Narendra Modi stated, “Honored to welcome the African Union as a permanent member of G20. This will strengthen the G20 and also strengthen the voice of the Global South.” This historic inclusion reflects India’s broader vision of fostering a multi-polar world in which power and decision-making are distributed more equitably among nations.The African Union, representing all 55 African states, serves as a critical platform for promoting unity, economic growth, and development across the continent. Africa, home to nearly 18% of the world’s population, possesses vast natural resources, a rapidly growing demographic base, and several of the world’s fastest-growing economies. By securing the AU’s place within the G20, India underscored the imperative of integrating African perspectives, challenges, and aspirations into global governance frameworks.This development also provides Africa with a valuable opportunity to further its Agenda 2063—an ambitious, strategic framework aimed at the socio-economic transformation of the continent over a 50-year period (2013–2063). The AU’s permanent membership in the G20 not only amplifies the voice of the Global South but also aligns with the principles of fairness, inclusivity, mutual respect, and shared responsibility in global affairs.
Moreover, addressing pressing global challenges such as climate change, migration, debt restructuring, food security, pandemic preparedness, and the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) requires the full participation of Africa. Without the continent’s involvement, meaningful and comprehensive solutions to these issues remain incomplete.India’s facilitation of the African Union’s entry into the G20 thus represents a transformative step toward more inclusive and representative global governance.
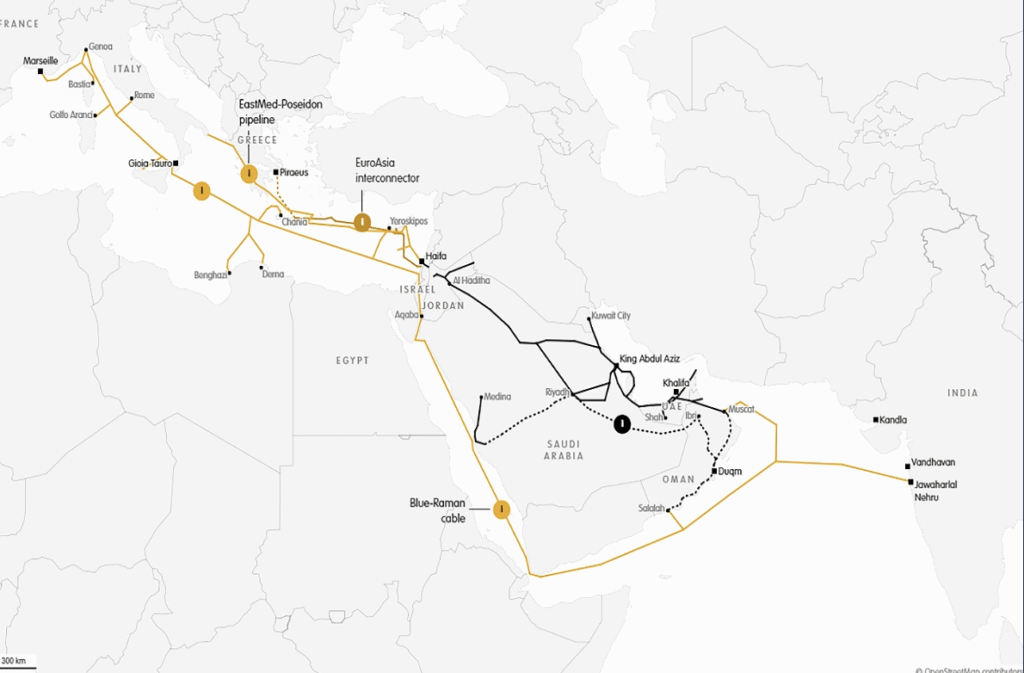
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEEEC)
The India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) was one of the landmark initiatives unveiled during India’s G20 Presidency in 2023. It reflects India’s growing influence in global geopolitics and its commitment to inclusive and sustainable development. IMEEEC is a strategic project aimed at enhancing maritime security and enabling faster movement of goods between Europe and Asia.U.S. President Joe Biden described the initiative as “a big deal and a game-changing investment” for the United States. The corridor links South Asia, the Middle East, and Europe, with strong strategic backing from the U.S. On September 9, 2023, a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was signed by India, the United States, the United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, France, Germany, Italy, and the European Union.IMEC supports the broader objectives of the Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment (PGII)—a global initiative launched by the G7 in 2021 to mobilize funds for sustainable infrastructure in developing countries—by translating these goals into a concrete regional connectivity project.The corridor passes through countries like Egypt, Morocco, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE, which have some of the world’s highest solar irradiance and wind energy potential, offering a solid foundation for green hydrogen production and clean energy cooperation.
While IMEEEC presents major opportunities to boost trade between India and Europe, it also comes with significant logistical and geopolitical challenges. Nonetheless, it has the potential to reshape the trade dynamics between Asia and Europe, currently dominated by routes passing through the Suez Canal.
India As Global South Leader
It is an undeniable reality that the international system remains dominated by the Global North, this is naturally reflected in the composition of the G20 as well.Through India’s G20 presidency endeavour is seek a re-globalization that is more diversified and democratic and it is only possible from economic growth and development, so developing countries need greater decision making power. Today’s major global challenges such as climate change, poverty, inequality, and their impact is greater on the countries of the Global South.The Ukraine conflict also had a negative impact on the developmental agenda of the Global south due to disruption of fuel, fertilizer, and food supplies which further worsen the precarious economic,social, and debt servicing conditions of many developing countries.Preserving the G20 as a bridge between North and South , between geopolitical rivals and rich and poor is an essential ingredient for tracking the transnational crises facing the world.The model of rotation in the presidency of the G20 allows countries of the south to exercise leadership and India’s presidency in 2023, the Brazilian presidency in2024 and South Africa’s presidency in 2025 will preference the Global South’s development priorities.
India’s leadership of the global south is underpinned by a strategy of multi-alignment,which allows it to maintain diverse partnerships while advancing the collective interests of developing nations.India hosted the Voice of the Global South Summit on January 12th and 13th 2023 under the theme “Unity of Voice, Unity of Purse”, as part of its efforts to amplify the concerns and aspiration of developing nations during its G20 presidency. Over 125 countries participated virtually,making it one of the largest ever gatherings of its kind.Leaders, ministers, and representatives from Asia, Africa, Latin America, the Caribbean, and the Pacific engaged in discussions.Opening remarks of Prime Minister Modi in Voice of Global Summit 12 January 2023 said that India provides an alternative narrative to global geopolitics by giving voice to the countries of the Global South, as three-fourths of humanity lives in these countries,and the Global South has the largest support in the world’s future. India inaugurated the center DAKSHIN.The aim of the center is to boost knowledge sharing and mutual learning for improving skills and enlargement sustainable, accessible, and locally relevant solutions by collating resources, experiences and strategies to overcome development challenges the Global South faces and promote globally inclusive partnership.India’s priorities for ensuring the Global South benefits from the global order are centered around equity, exclusivity, and sustainable development.Here’s an outline of India’s key priorities
- Advocating for Global Governance Reforms (UNSC,WB,IMF).
2. Climate Justice and Sustainability (Promote global alliances like International Solar Alliance and Mission Life, Green Energy).
3.Digital Transformation and Technology Sharing (UPI,CoWIN).
4.Food and Energy Security.
5.Economic Development and Debt Relief.
6.Accelerating Sustainable Development Goals.
India’s Digital Diplomacy: A Human-Centric Approach to Technology
India’s digital diplomacy Strategy during its G20 presidency showcased a modern, technology driven and human centric approach to the world promoting digital public infrastructure and transparency. As India’s G20 Sherpa Amitab Kant has said, “There are 400 million people do not have digital identity, 200 million people do not have a bank account,and 133 countries do not even have fast payments.This is a massive opportunity to use technology to transform the world.” By using India Stack (Aadhaar,e-KYC UPI,DigiLocker, Co-WIN) framework India has made significant growth in digital literacy. The initiative is a part of India’s Digital India mission, driving digital transformation across various sectors such as finance, governance and healthcare. India stack has become a model for other countries aiming to built similar digital public infrastructure.The G20 Digital Economy Ministerial Declaration further reinforces these focus areas, emphasizing the importance of Digital Public Infrastructure, Cyber security, Artificial Intelligence, cross-border data flows, and data governance in shaping an inclusive and resilient digital future.Through the sill India initiative India promotes skill based education and vocational training as a key agenda item shearing its own experiences and programs. It demonstrate how to utilize limited resources to achieve ambitious goal. The G20 Digital Economy working Group has point out three priority areas: digital public infrastructure, security in the digital economy, and digital skill. (The DEWG is led by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology) G20 Digital Economy Ministerial Declaration emphasized on Digital public infrastructure, Cyber security, Artificial Intelligence, cross border data flows, data governance.
India’s Soft Power and G20 Presidency
In another successful endeavor, during its presidency of the G20 India was able to showcase the country’s extensive and varied cultural traditions, from the performing arts and visual arts to heritage sites and food traditions, thereby providing a snapshot of the country’s cultural wealth and of cross-cultural understanding among the different countries represented at the summit. India’s G20 presidency is a projection of its soft power culturally but also economically in the cultural and tourism sectors, becoming a moment of national pride. India’s soft power was on display during its 2023 presidency of the G20, as he country positioned itself as a hub for diversity, democracy, culture, and tourism, as well as development, technology, and global leadership. For the first time every single state and union territory of India hosted G20 events, allowing each of them a chance to highlight the best of their culture. The event saw participation from over 17,000 artists and was organized by the Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR) with over 300 culture programs in over 60 locations. At the newly constructed summit space, Bharat Mandapam, a set of thematic exhibits. Among these is Bharat: Mother of Democracy, whose goal is to make clear that “the taking of the consent of the people, in governing one’s country has existed from the earliest recorded history” . There will also be a Digital India experience zone and crafts bazaar, of handicraft products from various regions of India with an emphasis on One District One Product (ODOP). Geographical Indication (GI) tagged products and products made by women and tribal artisans. Under India’s G20 presidency, the past few months have seen over 20,000 participants from over 115 countries join events across various locations in the world. India’s G20 presidency is a good opportunity to project Our democratic values, Economy, culture and tourism. This will hopefully make it a more desirable location for foreign investment and for relocating supply chains, building on the Atmanirbhar Bharat. India’s Ultimately, India’s G20 presidency was more than a series of high-level meetings—it was a celebration of democracy, diversity, and development. It reflected a confident nation eager to engage with the world on its own terms, sharing not just economic ambitions but also the values and cultural spirit that define the Indian identity.
India’s Presidency of G20 in 2023 was a “historic diplomatic moment” and a testament to the growing global influence of and leadership by India. It was precisely this cohesive, balanced and human-oriented approach that allowed India to overcome profound global rifts and foster collaboration while introducing the Global South’s perspective into mainstream geopolitics. The 18th G20 Summit which took place in New Delhi ,India in September 2023 saw the arrival of The African Union as permanent member of the Group, as well as some first that had never materialized at any of the earlier seventeen G20 summit including the launching of the Global Biofuel Alliance, the announcement of the IMEC economic corridor, the adoption of a Sanskrit-based theme for the summit , a G20 Green Development Pact with a concept of LiFE, With the G20 delivering a joint consensus declaration despite deepening global divides, the largest G20 outreach in history across 60 cities,and the Voice Of Global South Summit. Such initiatives were a distinct manifestation of India’s role and vision for greater global solidarity.
Following India, Brazil’s G20 presidency for 2024 has already outlined its main theme as “Building a just world and a sustainable planet.” Brazil’s presidency has set three main goals – Social Inclusion and the Fight against Hunger and Poverty, Sustainable Development, and Reform of Global Governance institution. Under Brazil’s new presidency, there is hope for a revival of more a human-centered understanding of development that connects economic growth not just with the economy, but with the people and the planet. Brazil as another important emerging economy and a key soul behind the Global South, is in a position to capitalize on what India has commenced, but will also bring its own perspective. The India and Brazil successive presidencies had the ability of bringing together two of the most relevant economies of the global south into a successful partnership that was the continuation and a sharper focus on some of the common challenges of developing nations. Though their respective agendas differ slightly in focus, the two are very compatible, and they provide a formidable global synergy for progressive change. Amplifying the voice of the Global South, Sustainable Development and climate Action, Inclusive Development and growth and inequality, reforms of multilateral institution, debt vulnerabilities. It is also Natural progression of ideas and initiatives for these presidents to follow one after another. While India has the strength of a abort consensus and ambitious targets, Brazil has arguably a strong platform for further deepening specific commitments and outcomes in social equity and environmental stewardship. It is this common commitment to tackle the worlds problem from a Global South perspective, what gives relevance to the G20 as a genuinely inclusive forum.
Conclusion
India’s Foreign policy believes on a multi polar world and multilateralism. India advocates for a world where no single country or bloc dominates global affairs. A multi polar world ensures greater stability and fairness in the international system. The 5 S’s of multilateralism Samman(Respect),Samvad(Dialogue),Sahyog(Cooperation),Shanti(Peace),Samriddhi(Prosperity), a guiding philosophy for India’s G20 presidency .Nationalism, Protectionism, Unilateralism is threat to multilateralism so India align with the philosophy of Vasudhaiva Kutumbakum – the world is one family, and these principles reinforce the need for a collaborative global approach to tackle pressing challenges in a polarized world.India’s foreign policy, especially in recent years, has increasingly emphasized the idea of the “global common good,” reflecting its commitment to being a responsible global actor. During its G20 presidency, the Indian government has sought to use this concept to guide efforts in finding long-term solutions to some of the world’s most pressing challenges—many of which stem from deepening global interdependence. These challenges include climate change, emerging technologies, food and energy insecurity, and more.
Prime Minister Narendra Modi at the G20 Foreign Ministers’ Meeting on March 2, 2023 said that “We should not allow issues that we can not resolve together to come in the way of those we can.As you meet in the land of Gandhi and the Buddha,I pray that you will draw inspiration from India’s civilizational ethos to not on what divides us, but on what unites us”. India’s G20 theme Vasudhaiva Kutumbakum- One Earth(Focus on sustainable environment practices and combating climate collectively),One Family(Stresses exclusivity, equity and solidarity among nations, particularly between developed and developing countries),One Future( build a secure equitable and prosperous world for future generation through innovation and cooperation) aim is to popularize Indian ancient ethos of universal brotherhood, interdependence and global unity.
References:
1. Ali, M. A., & Kamraju, M. (2023). The G20 Presidency of India in 2023: Achievements, Challenges, and Implications. International Journal of Business and Management Research, 11(4), 100-106.https://ijbmr.forexjournal.co.in/archive/volume-11/ijbmr-110401.html
2. https://wwwindia.gov.in, accessed on November, 12, 2024.
3. https://en.wikipedia.org, accessed on November, 23, 2024.
4. https://g20.org, accessed on November, 25, 2024.
5. https://g20.mygov.in, accessed on November, 18, 2024.
6. https://www.india.gov.in, accessed on November, 20, 2024.
7. https://en.m.wikipedia.org, accessed on November, 22, 2024.
8. Mukherjee, B . (2022).India and the G20 presidency :Its priorities and challenges .India Foundation,Ⅲ(6),November,(15-23).https://indiafoundation.in/articles-and-commentaries/india-and-the-g20-presidency-its-priorities-and-challenges/
9. Nahak, D.(2023). India’s G-20 Presidency and Changing World Order. International Journal of Professional Development,12,( 1) Jan-June,(60-65),:https://www.ijpd.co.in/papersv12n1/14.pdf.
10. Pillai, M. B.(2024). The Global South: Together for a Shared Future. ISDA JOURNAL,34,(3),(153-159). : https://isdajournal.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/The-Global-South-Together-for-a-Shared-Future
11. Pandey, R. S., & Shukla, S. (2023). Perspective of G20 along with India’s cultural values. Knowledgeable Research: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 1,(09), April,( 59-70). http://www.knowledgeableresearch.com
12. Warwantkar, S. (2023). India’s G20 Presidency: Challenges and Opportunities. Vidya-A Journal of Gujarat University, 2(1), January-June, pp.48- 52, accessed at, https://vidyajournal.org/index.php/vidya/article/view/134.
13. www.g.20.org/en/, accessed on November, 26,2024.